Electrical Wiring Basics in the UK: Colours, Circuits, Safety, and Smart Upgrades
Electrical Wiring Basics in the UK: Colours, Circuits, Safety, and Smart Upgrades
If a tripped breaker, dead socket, or flickering light has you reaching for the fuse box, a little wiring knowledge goes a long way, especially when waiting on an electrician isn’t an option. By grasping colour codes, circuit types, and core safety protections like RCDs, you can spot issues early, communicate clearly with professionals, and keep minor fixes from turning into safety risks.
Understanding Electrical Wiring
Before touching any cable, know how to identify conductors, select the right cable type, and follow the current edition of BS 7671 for safety and compliance in the UK. Most homes are wired to modern standards, but older properties can mix legacy and new colour systems, so correct identification and labelling are essential for safe work.
UK Electrical Wire Colour Coding
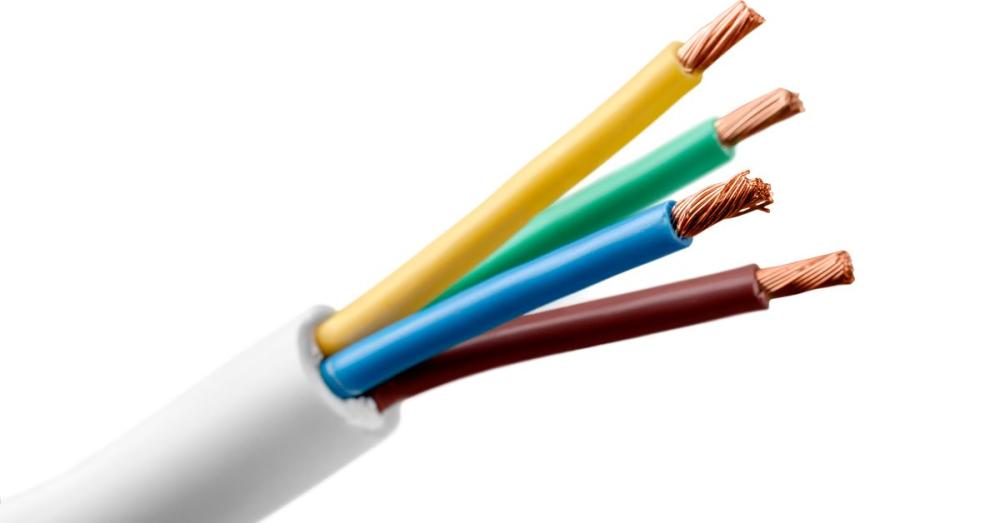
In UK domestic AC wiring, today’s colours are harmonised with European standards: brown for line (live), blue for neutral, and green/yellow for protective earth, adopted nationally by March 2006. Properties wired before full adoption may still use red for live and black for neutral, so never assume colours, verify with testing and labelling if both systems are present.
Green/Yellow Earth Wire
The earth conductor provides a low-resistance path that clears faults quickly by operating protective devices, reducing shock and fire risk in the event of insulation failure. The earth colour remained green/yellow through harmonisation to maintain continuity and reduce confusion in safety-critical identification.
Brown Live Wire
The live conductor supplies energy from the source to the load, and contact can be lethal even when a circuit appears “off,” so isolation and testing are mandatory before work. Correct identification of the live ensures safe termination in devices, accessories, and protective equipment rated for the intended load.
Blue Neutral Wire
Neutral completes the circuit back to the supply and can still be dangerous relative to earth if the system is faulted or incorrectly isolated. Treat neutral connections with the same care as live conductors and verify dead with an approved tester before contact.
Source - TVE
Old UK Wire Colours
Older UK installations often use red for live, black for neutral, and green/green‑yellow for earth, and these may remain serviceable if safe and tested. Where alterations are made, the new work must comply with current BS 7671, and mixed colours require clear warnings and labelling at the consumer unit.
Why the Wiring Colours Changed
The UK harmonised with IEC-aligned colours starting 2004, with full compliance required for new work after 31 March 2006 to improve clarity and cross‑border consistency. The change aimed to reduce errors across European-sourced products and documentation while preserving the distinctive earth colour.
Core Elements of a Domestic Electrical Circuit
Modern domestic installations centre on a consumer unit with a main switch, MCBs for overcurrent protection, and RCDs for additional shock protection across most circuits. Circuits are typically arranged as ring final circuits or radials, with dedicated supplies for high‑load appliances as required by design and BS 7671.
Consumer Unit (Fuse Box)
The main switch isolates the entire installation; MCBs protect individual circuits from overloads and short circuits by automatic disconnection of supply. RCDs or RCBOs provide life‑saving disconnection on earth faults and are required on most domestic circuits under current regulations.
The Cables
Twin and earth cables carry live and neutral with a CPC (earth), with modern sizes and sheathing types selected for load, route, and installation method per BS 7671. Regular inspection is wise, as insulation and terminations deteriorate; many domestic rewires are considered around the 30–40 year mark based on condition and test results.
Radial Circuits
A radial circuit runs from the consumer unit to outlets in a single path and ends at the last point, sized to the protected load and floor area served. Radials are often used for dedicated appliances, outdoor supplies, or where layout suits a straight run rather than a loop.
Ring Final (Ring Main) Circuits
A ring final circuit loops out and back to the consumer unit, sharing load in two directions and enabling more sockets with efficient copper use up to about 100 m² per ring. Correct load distribution and good joints are essential; poor connections can unbalance the ring and risk overloading a single leg.
Spurs
A spur is a short branch from a ring or accessory; an unfused spur typically serves a single outlet, while fused connection units can supply more downstream points safely. Keep the total number of spurs sensible relative to ring outlets and ensure conductor and CPC integrity when adding spurs.
Dedicated Appliance Circuits

High‑demand loads like cookers, showers, and immersion heaters normally require their own radial circuits, matched with higher‑rated breakers and suitable cable sizes. Two‑pole isolation and appropriate control units are standard practice for safe maintenance and emergency switching on fixed appliances.
Earthing and Bonding
Earthing connects exposed conductive parts to earth so protective devices disconnect dangerous faults quickly, reducing shock risk. Main protective bonding links incoming metallic services (e.g., water and gas) to the earthing system to prevent dangerous potential differences across touchable metalwork.
Electrical Wiring Connections: Single-Phase vs Three-Phase
Most UK homes are single‑phase 230–240 V with one live, one neutral, and earth, which suits lighting and standard domestic appliances. Three‑phase at 400–415 V is typical in commercial or industrial settings and some larger residences, providing three live phases for higher and more balanced power delivery.
Wire Sizing and Current Capacity
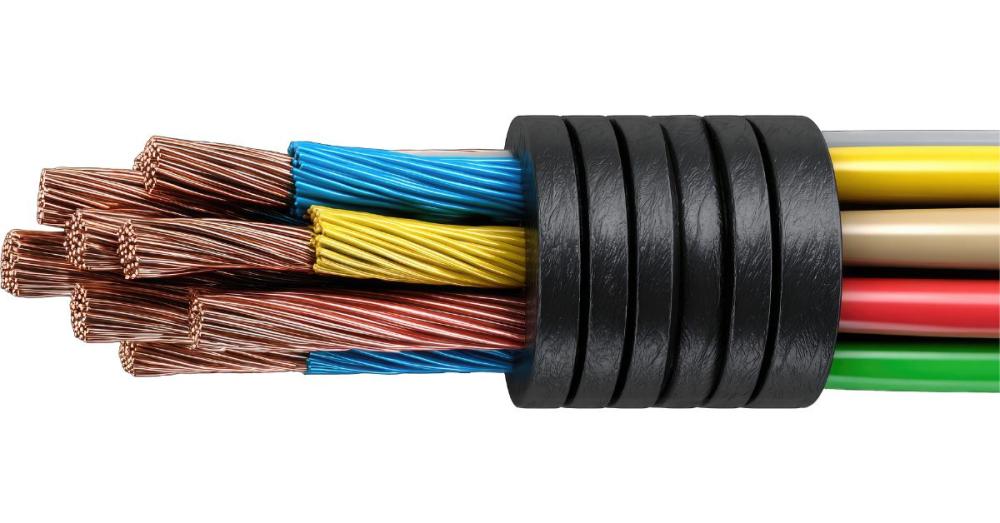

Wire size refers to the conductor cross‑section and determines current‑carrying capacity, voltage drop, and protective device coordination. Selecting the wrong size risks overheating and fire; sizing must consider installation method, grouping, ambient temperature, and protective device ratings per BS 7671.
Common Cable Types You’ll Encounter
- Communication/data cables: Low‑voltage, low‑current cabling for networking and signals, distinct from power cables in construction and use cases.
- Direct burial cable: Moisture‑resistant sheathing suitable for underground runs where permitted, typically with additional protection based on local requirements.
- Fire‑resistant/LSZH cables: Maintain critical circuits during fire and limit smoke/halogen emissions for safer evacuation and emergency response.
Do You Need Trunking or Conduit?
Metal or uPVC trunking and conduit protect cables, provide neat routing, and help maintain fire compartmentation when installed with compliant fittings and seals. Good cable management reduces damage, mix‑ups, and nuisance faults, while also supporting compliance with wiring routes and depth regulations.
Safety, Testing, and RCDs
RCD protection is required on most domestic circuits today, including sockets and bathroom circuits, with specific rules when extending existing circuits near baths or showers. Always test for dead before work, use appropriate isolation, and engage a qualified electrician for alterations subject to regulation and certification.
Practical Tips for Homeowners
- Label the consumer unit clearly, especially where mixed colours exist, and keep test reports accessible for future work.
- If you notice tripping, heat at outlets, or discoloured accessories, stop use and have a qualified electrician investigate promptly.
- Plan loads: kitchens often concentrate heavy appliances, check ring balance or opt for dedicated radials to avoid nuisance trips.
Conclusion
Understanding wiring colours, circuit design, and protections like RCDs makes your home safer and your conversations with electricians clearer, while reducing the risk of DIY errors.
For compliant cables, consumer unit upgrades, fire‑safe management, and professional‑grade accessories, shop Meteor Electrical for trusted brands, fast delivery, and expert support. Power your project with confidence today.
FAQs
Q1: What are the current UK wiring colours?
Brown (live), blue (neutral), and green/yellow (earth) for single‑phase domestic circuits under harmonised standards since 2006.
Q2: Are old colours like red and black still legal?
They may remain in older installations, but any new work must use the harmonised colours, and mixed systems require clear labelling at the consumer unit.
Q3: Do all socket circuits need RCD protection?
Under current BS 7671 practice, most domestic circuits, including socket outlets, require RCD or RCBO protection for additional shock safety.
Q4: Ring main or radial, what is better?
Rings efficiently serve larger floor areas up to about 100 m², while radials suit dedicated loads, outbuildings, or simpler layouts, design and load decide.
Q5: What is bonding and why is it important?
Bonding connects incoming metal services to the earthing system to prevent dangerous voltage differences between touchable metal parts during faults.
Q6: When should a rewire be considered?
Condition and test results drive the decision; older installations often benefit from updates where insulation, earthing, RCD coverage, or accessories show age‑related deterioration.