Demystifying Electric Wiring: Understanding Different Types of Electrical Wiring and Cables
Demystifying Electric Wiring: Understanding Different Types of Electrical Wiring and Cables
When it comes to any kind of building, be it a home, office, or industrial space, the electrical wiring is the invisible yet essential nervous system. It powers your lights, appliances, heating systems, and technology. But here's the thing: not all wires and cables are created equal. Understanding the different types of electrical wiring and cables is key to making sure your system is not just functional, but also safe, efficient, and regulation-compliant.
Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast working on a home renovation or a professional contractor handling larger installations, getting familiar with the wiring types available can help you avoid costly mistakes and potentially hazardous situations.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know, from how to choose the right wiring and what makes one cable different from another, to understanding UK wire colour codes and circuit types. This guide aims to provide both clarity and confidence for your next electrical project.
Understanding Electrical Wiring
Before diving into an electrical installation or upgrade, it’s essential to know the basics. That means recognising different cable types, knowing what each one is used for, and understanding the regulations that govern their use.
Every electrical project should start with one core principle: safety. Familiarising yourself with UK electrical codes, especially the BS 7671 guidelines is the first step. These standards ensure that any installation meets national safety and performance requirements.
It’s also crucial to understand the materials involved. Each cable type has specific characteristics, such as conductor material, insulation type, and flexibility, which determine its suitability for various applications.
Whether you're fitting an outdoor lighting system or installing sockets in a kitchen, identifying the right cabling will help prevent short-circuiting, overloads, and potential fire hazards.
Choosing the Right Electrical Wiring
Electrical wiring isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. In fact, it's the opposite. There are many factors to consider when choosing the right wire, including conductor type, environment, and current load. Let’s break it down.
Conductor Material
The conductor material inside the wire plays a crucial role in performance. Here's a look at the most commonly used types:
- Copper Cable: Known for its excellent conductivity and durability, copper is the go-to choice for most residential and commercial applications.
- Aluminium Cable: While not as conductive as copper, aluminium is lighter and often used in larger-scale electrical transmission.
- Steel Cable: Found in steel wire armoured (SWA) cable, this material adds extra protection, especially in outdoor or underground installations.
Each type of conductor has its pros and cons, but copper wiring remains the most widely used due to its efficiency and flexibility.
The Cable’s Intended Function
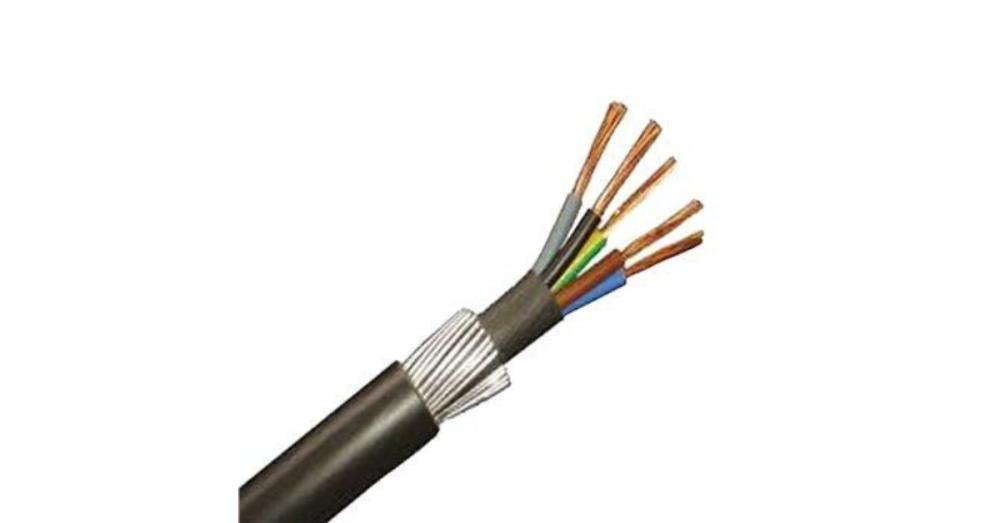

Understanding the cable’s function is just as important as the material itself. Different environments require different types of protection.
- General Purpose Cabling is great for basic household wiring and small appliances.
- Submersible Cable is waterproof and perfect for pumps or underwater equipment.
- Armoured Cables such as SWA cable are designed for rugged environments like construction sites or underground trenches.
By identifying the environment in which the cable will operate, you’ll be better equipped to choose a cable that ensures safety and longevity.
Cable Core Count
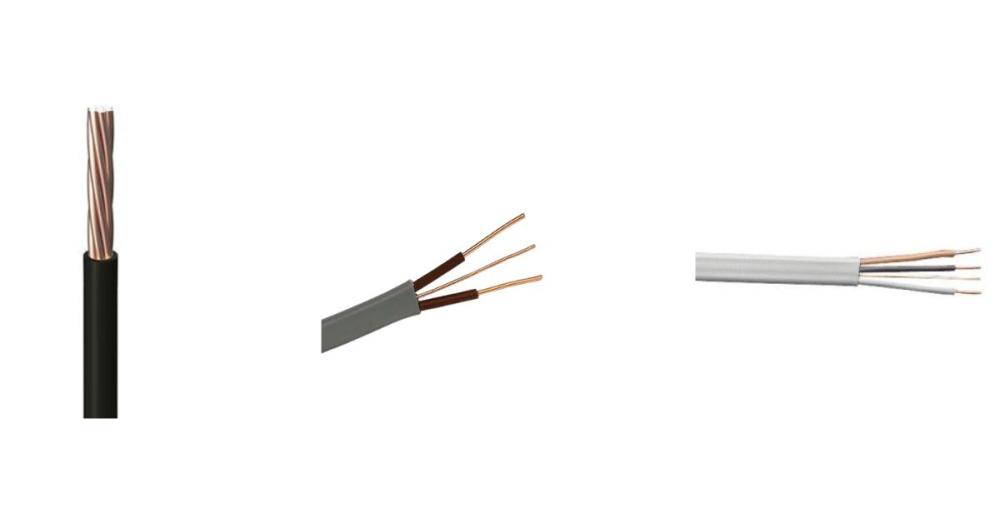
The number of cores in a cable refers to the individual conductors within the cable. These cores determine how much power the cable can carry and how it interacts with other system components.
- Single Core Wiring: Used for simple, low-load applications.
- Two-Core Cable: Typically includes a live and a neutral wire, ideal for lighting circuits.
- Three-Core Cable: Adds an earth wire, which is important for safety in appliances and outdoor installations.
- Multi-Core Cable: Used in more complex setups like data transmission and machinery.
Choosing a three-core cable with earth is recommended for most residential and light commercial setups.
What Are the Different Types of Cables?

Now that you know what to consider, let’s look at the different types of cables you’ll come across in real-world applications.
Communication Cables
These are specialised cables used for transferring information rather than power. Think of internet lines, alarm systems, and telephone connections.
Unlike power cables, communication cables are designed for low current and low voltage operations. Their purpose is to deliver clear and consistent signals over varying distances whether it's a short span across your living room or a long haul between networked buildings.
Common uses include:0
- Ethernet and LAN networks
- CCTV camera systems
- Data transmission for smart homes
Direct Burial Cable
If you’re installing wiring outdoors or underground, standard indoor cables won’t cut it. You’ll need a direct burial cable.
These cables are engineered with tough, moisture-resistant sheathing that protects the internal wiring from soil pressure, water ingress, and general wear and tear. In some cases, these can be laid without conduit, although it’s always wise to check your local building regulations first.
SWA cable is a common choice here, thanks to its built-in steel armour that protects against mechanical damage.
Fire-Resistant Cables
In critical situations, power can mean the difference between safety and disaster. That’s where fire-resistant cables come in.
Designed for emergency systems like fire alarms, smoke detectors, and voice alarms, these cables maintain electrical integrity even during a fire. They're usually wrapped in mica tape, a fire-retardant material, and are often halogen-free to reduce smoke emission.
Such cables are vital in hospitals, schools, and other buildings where evacuation and emergency systems must stay functional during fire outbreaks.
Understanding Electrical Wire Colour Coding
Wire colour codes are not just cosmetic, they’re essential for safety and organisation. In the UK, colour coding is used to distinguish between live, neutral, and earth wires, helping electricians and installers quickly identify the correct connections. These colours are also crucial for keeping your electrical system organised and maintained.
Here’s what you’ll typically see:
- Green and Yellow: Earth wire, critical for preventing electric shocks
- Brown: Live wire carries current from the source to the device
- Blue: Neutral wire returns current back to the source
It's also worth noting that the colour coding can vary between older and newer buildings. Before 2006, the live wire was red and the neutral was black. Since then, the UK adopted new colours in line with European harmonisation regulations.
Though older buildings aren’t legally required to be updated, any new installations or major rewiring must comply with the post-2006 colour codes, as specified in BS 7671.
Source- TVE
What Are Electrical Wiring Connections?
Knowing the wiring types is one thing, understanding how they connect is another. There are two main types of electrical connections you should know:
Single-Phase Wiring
This is the standard setup for most homes and small offices. It includes one live wire, one neutral, and one earth. It runs at 230–240V and powers everything from lighting to TVs to kitchen appliances.
Because it’s easy to install and cost-effective, it’s the go-to solution for residential electrical needs.
Three-Phase Wiring
If you’re powering large-scale machinery or industrial systems, single-phase won’t cut it. You’ll need a three-phase system, which offers more consistent power and higher voltage (typically 415V in the UK).
This setup uses three live wires and may include a neutral and an earth, depending on the configuration.
It’s commonly used in:
- Warehouses
- Factories
- Commercial kitchens
- Industrial-grade HVAC systems
What Is Wire Sizing?

One of the most overlooked aspects of wiring is choosing the correct wire size or gauge. The wire size determines how much electrical current the conductor can carry safely. Too small, and you risk overheating. Too large, and you're wasting money and space.
Wire size is usually measured in mm² in the UK. Factors to consider include:
- The current load
- The length of the wire
- The type of load (resistive or inductive)
As a general rule, 2.5mm² twin and earth cable is used for socket circuits, while 1.5mm² is suitable for lighting. Always refer to a trusted sizing chart or consult an electrician before making a final decision.
What Are the Important Elements in an Electrical Circuit?
Once you’ve selected the right wire and cable, the final step is integrating them into the correct circuit type. In the UK, circuits typically fall into three categories:
Consumer Unit
Also known as a fuse box, the consumer unit is the central hub of your home’s electrical system. It includes:
- Main Switch – Controls the overall power supply
- MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) – Protect individual circuits
- RCDs (Residual Current Devices) – Monitor for faults and cut power to prevent shock or fire
Proper labelling and organisation in the consumer unit make repairs and upgrades safer and faster.
Source- Cognito
Radial Circuit
A radial circuit is a simple setup where wires run in a straight line from the consumer unit to the end device. While easy to install, this layout is limited in the number of sockets or appliances it can handle.
Ring Main System
A ring main forms a loop, beginning and ending at the consumer unit. This configuration allows current to flow in two directions, improving efficiency and load capacity.
Ring mains are common in UK homes and are typically used for powering multiple outlets within a single room or area.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right wiring might not be the flashiest part of an electrical project, but it is undoubtedly one of the most important. From understanding UK electrical wiring colour code changes to selecting the right steel wire armoured SWA cable, every decision contributes to the safety and success of your installation.
At Meteor Electrical, we stock a comprehensive range of high-quality cables, from fire-resistant options to three-core cable with earth, all designed to meet modern safety standards. Plus, with next-day delivery across the UK, you get the reliability you need to keep your projects running smoothly.
Whether you're a first-time DIYer or a seasoned pro, let Meteor Electrical be your trusted partner in powering your next project.
Ready to get started? Shop all cables now and take your electrical installations to the next level.
FAQs
1. What are the different types of electrical cables used in UK homes?
The most common types of electrical cables used in UK homes include twin and earth cables, armoured SWA cables, three-core cables with earth, and flexible cords. Each serves different functions depending on power load, installation environment, and safety requirements.
2. What is the difference between single-phase and three-phase wiring?
Single-phase wiring uses one live wire and is ideal for homes and small offices, delivering 230–240V. Three-phase wiring uses three live wires (sometimes with a neutral and earth) and is designed for heavy-duty appliances and industrial setups, offering 415V.
3. What does the colour coding of electrical wires mean in the UK?
In the UK, the standard wire colour codes are: brown for live, blue for neutral, and green/yellow for earth. These colours help identify wire functions and ensure safe installation. Older systems may use red (live) and black (neutral).
4. When did UK electrical wiring colours change?
The UK wiring colour codes changed in April 2006 to align with European standards. The new colours include brown (live), blue (neutral), and green/yellow (earth). This change was outlined in the BS 7671 Wiring Regulations.
5. Can I bury electrical cable directly in the ground?
Yes, you can use a direct burial cable or steel wire armoured (SWA) cable for underground installations. These are designed to resist moisture and physical damage. Always follow local building codes when planning underground wiring.
6. What is the purpose of a three-core cable with earth?
A three-core cable with earth includes live, neutral, and earth conductors. It’s used for appliances or installations that require grounding for safety, such as outdoor lighting, kitchen appliances, and power tools.
7. What size electrical cable do I need for sockets and lighting?
For UK homes, 2.5mm² twin and earth cable is typically used for socket outlets, while 1.5mm² is used for lighting circuits. Always verify your wire size based on load requirements and distance to avoid voltage drop or overheating.
8. What is the safest cable to use in case of fire?
Fire-resistant cables, often made with mica tape insulation and halogen-free sheathing, are the safest option in fire-prone areas. They maintain functionality during a fire and don’t emit toxic smoke, making them ideal for emergency systems.

