Power Up Right: A Practical Guide to Electrical Cable Sizing
Power Up Right: A Practical Guide to Electrical Cable Sizing
In the intricate world of electrical systems, selecting the correct cable size isn't just a best practice, it's a non-negotiable safety measure. Whether you're installing lighting in your home or designing a commercial setup, the right cable ensures system efficiency, reduces risk, and boosts reliability.
According to the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) and Electrical Safety First, incorrect cable selection can lead to overheating, short circuits, or even fires. At Meteor Electrical, we believe in powering systems the smart way.
This guide breaks down the core principles of cable sizing, from capacity and voltage regulation to environmental suitability.
Why Choosing the Right Cable Size Matters

The primary role of an electrical cable is to transmit current efficiently and safely. Choosing the right size ensures:
- Minimal resistance
- Better performance
- Long-term safety
The wrong size? That can result in serious failures, including damaging equipment, endangering lives, and breaching UK wiring regulations.
Consequences of Incorrect Cable Sizing

- Overheating: Undersized cables can’t handle higher loads, causing insulation to melt and posing serious fire risks (ElectriciansForums).
- Electrical Fires: Increased resistance leads to heat build-up and sparks (Fire Safe Advice Center).
- System Failures: Poor connections and short circuits are often the result of incorrectly sized cables. (TheEngineeringToolbox).
Key Factors in Cable Sizing

1. Current Carrying Capacity
This refers to how much current a cable can safely carry without excessive heating. Refer to the British Standards BS7671 wiring regulations for baseline guidance.
2. Voltage Regulation
Voltage drop should ideally not exceed 5%. Cables must be sized to prevent energy loss and maintain appliance efficiency, particularly for long cable runs or high-demand systems.
3. Short Circuit Rating
This is a cable’s ability to withstand a short-circuit current for a defined period. This factor ensures that the cable doesn't fail catastrophically before the circuit breaker trips.
Pro Tip: Always refer to official manufacturer data sheets for exact ratings, especially on critical installations.
Understanding Wire Size and Gauge

Wire gauge (measured in mm² in the UK) reflects both current capacity and physical thickness. The lower the gauge, the thicker the wire, and the higher the current it can safely carry. Choosing the wrong gauge could mean undersupplying your system or compromising safety.
Tips for Determining the Correct Cable Size
- Use the BS7671 standard or a certified cable calculator
- Measure voltage drop over expected distance
- Account for ambient temperature and installation method (conduit, clipped, buried)
Source- eFIXX
Additional Factors to Consider
Installation Location
Environment greatly affects performance. For example:
- Outdoor installations may require armoured or water-resistant cables
- Indoor spaces demand flexibility and heat resistance
RS Components offers reliable specs for environmental cable suitability.
Cable Construction
Choose between:
- Single-conductor cables: Easy to install, more common in domestic setups.
- Three-conductor cables: Includes earth wire; perfect for circuits that need grounding.
Insulation Covering
Harsh environments require tougher sheathing. If you’re dealing with chemical exposure, rodents, or high moisture, opt for reinforced insulation like LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen).
Common Types of Domestic Cables in the UK
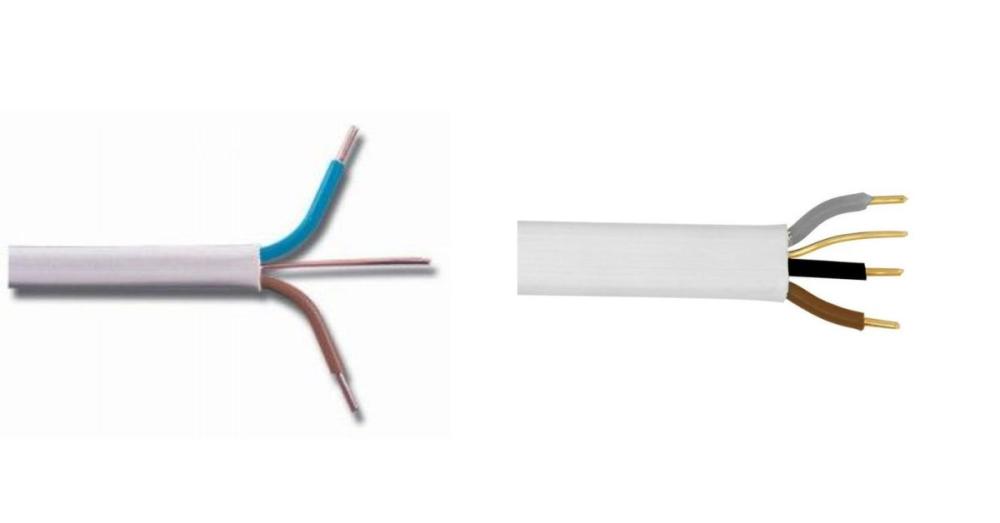
Twin Core and Earth Cables
Standard for lighting and power circuits, with PVC sheathing.
3-Core and Earth Cables
Used in two-way lighting systems, offering more configuration options.
Armoured Cables (SWA)
Perfect for underground power supply. They provide mechanical protection and are available in a wide range of sizes.
Communication Cables
Designed for low voltage data transmission, ideal for home networks and smart systems.
Direct Burial Cable
Suited for underground installation without conduits. Look for UV-resistant and moisture-rated variants.
Fire-Resistant Cables
Crucial for emergency lighting and alarm systems. These maintain functionality during fires and comply with BS7671 safety regulations.
Ensuring Electrical Safety
When it comes to electrical work, cable sizing and compliance with safety standards go hand in hand. Incorrect sizing increases the risk of:
- Electric shock
- Arc flashes
- Damage to expensive appliances
Visit HSE.gov.uk for a full breakdown of electrical safety laws and regulations in the UK.
Source- Schneider Electric
Benefits of Following Cable Sizing Guidelines
- Enhanced safety in domestic and commercial systems
- Longer system lifespan with minimal downtime
- Lower energy loss, leading to cost savings
Conclusion: Choose Cable Sizes Confidently with Meteor Electrical
Selecting the right cable size is more than just a box to tick, it’s a key component of a safe, reliable electrical system. By understanding current capacity, voltage drop, short circuit rating, and installation environment, you can confidently power your projects.
At Meteor Electrical, we stock a wide range of twin core, armoured, fire-rated, and data cables, all sourced from leading manufacturers and compliant with UK standards. Whether you're a seasoned electrician or taking on a DIY project, our expert team is here to support you every step of the way.
Shop high-quality electrical cables and accessories now at Meteor Electrical, your trusted supplier for safe and efficient electrical solutions.
FAQs
1. What is the correct cable size for domestic electrical wiring in the UK?
The correct cable size depends on the current load, length of the run, and installation environment. For typical lighting circuits, 1.5mm² twin and earth cable is standard, while 2.5mm² is used for socket circuits. Always follow BS7671 wiring regulations or consult a qualified electrician.
2. How do I calculate the right cable size for my electrical installation?
To calculate cable size, factor in the current carrying capacity, voltage drop limit (usually 5%), installation method, and short circuit rating. You can use a cable sizing calculator or refer to British Standard tables for accurate sizing.
3. Why is voltage drop important when selecting cable sizes?
Voltage drop affects the performance and safety of your electrical system. A cable with too much voltage drop can cause lights to dim or appliances to malfunction. UK regulations recommend a maximum drop of 5% for most domestic and commercial circuits.
4. What happens if I use the wrong size electrical cable?
Using an undersized cable can lead to overheating, fire hazards, and equipment failure. Oversized cables, while safer, can be unnecessarily expensive and difficult to install. Always match the cable to the circuit’s load and application.
5. Can I use the same cable type for indoor and outdoor installations?
No, outdoor installations require cables like SWA (Steel Wire Armoured) that are designed to withstand moisture, mechanical stress, and environmental exposure. Indoor cables typically use PVC insulation, which isn’t suitable for harsh outdoor conditions.
6. What is the difference between single-core and three-core cables?
Single-core cables contain one conductor and are ideal for simple installations or conduit work. Three-core cables include live, neutral, and earth conductors, making them suitable for two-way switching systems and providing extra safety in domestic wiring.

