Keeping the heat in
Keeping the heat in

As winter temperatures continue to dip across the UK and Ireland, keeping your home warm without driving up energy bills is more important than ever. According to the UK Department for Energy Security and Net Zero, households lose up to 25% of their heat through the roof and 35% through walls and gaps. This not only leads to discomfort but also unnecessary spending.
At Meteor Electrical, we know that small changes can make a big impact when it comes to heat efficiency. By addressing common sources of heat loss, you can make your home more comfortable, reduce condensation issues, and significantly lower your energy consumption.
So, what are the main types of heat loss, and how can you stop them? Let us guide you through practical, affordable solutions to make your home cosier and more energy-smart in 2025.
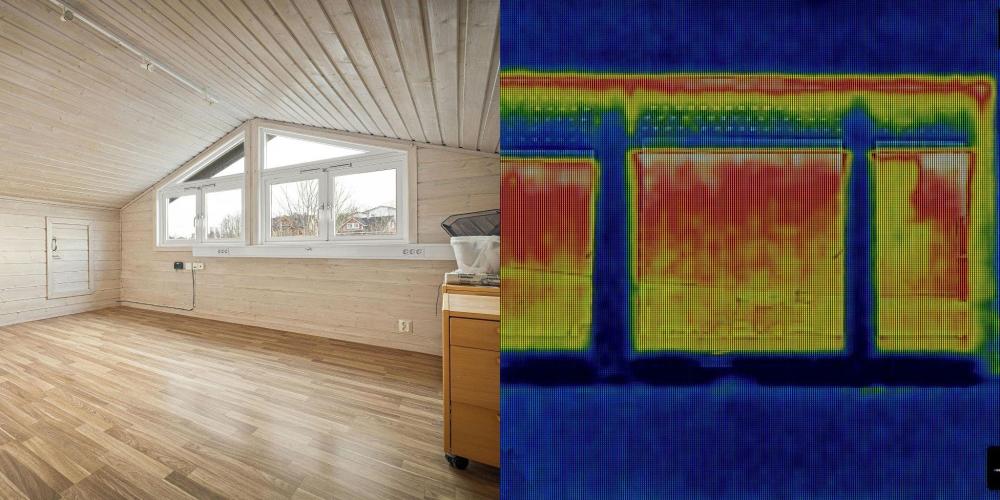
Understanding Heat Loss: Fabric vs. Ventilation
There are two primary ways your home loses heat:
1. Fabric Heat Loss
This refers to heat escaping through the structure of your home—walls, floors, windows, and especially the roof. Materials like concrete, bricks, and wood all allow heat to pass through, albeit at different rates.
2. Ventilation Heat Loss
This occurs through air movement, both intentional (like vents and extractor fans) and unintentional (gaps in windows, under doors, etc.). While some airflow is needed to avoid damp and condensation, uncontrolled draughts are a major culprit of heat loss.
Credit: CHIRANJEEVI RAHUL ROLLAKANTI
1. Draught Proofing: A Small Fix with Big Results
Did you know that a typical UK home loses around 15% of its heat through draughts?
Draught proofing is one of the most cost-effective ways to improve your home’s heat retention. Focus on sealing:
- Window frames
- Doors
- Letterboxes
- Loft hatches
- Pipework and wall outlets
You can use compression seals, foam strips, or gun-applied silicone sealants to plug the gaps. According to Energy Saving Trust, draught-proofing windows and doors can save the average household around £45 annually.
2. Loft Insulation: Stop Heat from Escaping Upwards
Since heat rises, the attic is a major area of heat loss—up to 25%, in fact.
Installing loft insulation acts as a thermal barrier, helping to trap heat inside your living space. You can choose from:
- Mineral fibre quilts (most common and budget-friendly)
- Loose fill insulation (great for irregular spaces)
- Natural insulation materials like sheep’s wool
While insulation may cost a few hundred pounds upfront, it can save you around £150–£250 per year on energy bills depending on your home type.
3. Window Insulation: Upgrade the Glass
Windows are responsible for around 18–20% of heat loss in most homes. Improving your windows' insulation is a long-term investment in both comfort and energy savings.
Options include:
- Double glazing (standard in most modern homes)
- Secondary glazing (budget-friendly and effective for older homes)
- Thermal curtain liners or heavy drapes
These methods improve your windows’ U-value (the rate at which heat passes through materials). The lower the U-value, the better the insulation.
4. Avoiding Condensation: Better Ventilation Matters
Condensation does not just damage walls and windows—it also increases humidity, making your home feel colder and harder to heat.
To manage it:
- Install extractor fans in kitchens and bathrooms
- Use trickle vents in windows
- Keep internal doors closed while cooking or showering
If left unchecked, condensation can lead to mould, poor air quality, and insulation damage. Be proactive in keeping your home dry and ventilated.
5. Use Smart Heating Controls
Smart thermostats and programmable heating timers allow you to heat your home more efficiently—only when and where it is needed.
Benefits of using smart heating systems:
- Control from your smartphone
- Set room-by-room temperatures
- Optimize heating schedules for weekdays vs. weekends
Many of these devices also give you data on your energy usage, so you can adjust for better savings. Meteor Electrical offers a range of smart heating solutions to help with this.
Credit: Home Caprice
Conclusion: Small Changes, Big Comfort
Heat efficiency is not about overhauling your home—it is about making small, smart improvements that protect your comfort and your wallet. From loft insulation to draught-proofing and smarter window solutions, there are many affordable ways to retain warmth in your home.
With energy costs still a major concern in 2025, improving your home’s insulation and ventilation is a smart investment. Explore Meteor Electrical’s heating and energy-saving products to get started today.
Let your home work with the cold—not against it.

