The Ultimate Guide to Consumer Units: Protecting Your Home and Business
The Ultimate Guide to Consumer Units: Protecting Your Home and Business
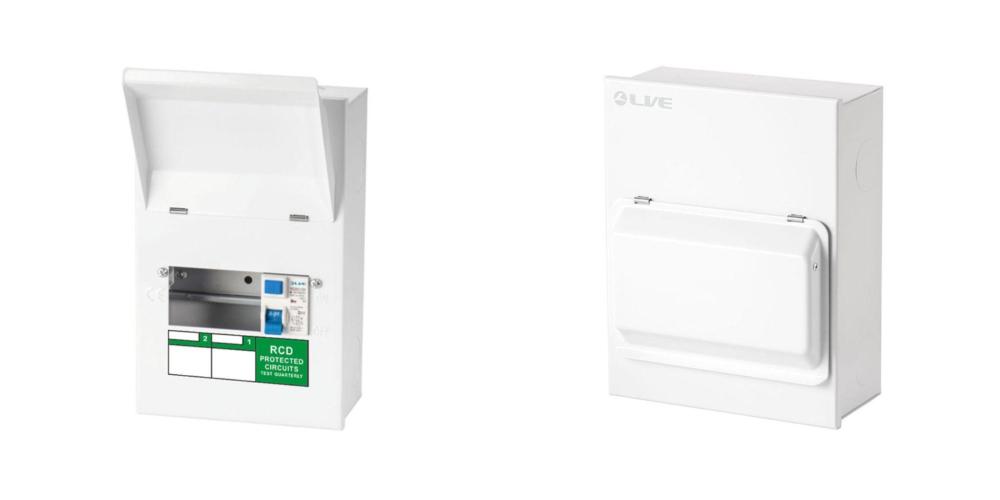

Have you ever wondered what a consumer unit is and why it matters? Whether you own a home, manage a business, or oversee a renovation project, a consumer unit — often referred to as a fuse box — plays a critical role in electrical safety. It’s not just a box of switches; it’s the control hub that protects you, your family, and your appliances from electrical hazards.
In this guide, we'll break down what a consumer unit is, how it works, and why it’s essential for your property. We’ll also explore the key components, different types available, and UK & ROI regulations to ensure your setup is safe and compliant.
Need official safety info? Visit Electrical Safety First and the IET Wiring Regulations for further reading.
What is a Consumer Unit?

A consumer unit, or fuse box, is the nerve centre of your electrical system. Its job is to control and distribute electricity safely throughout your property. Located near the electricity meter, the consumer unit houses critical components like the main switch, RCDs (Residual Current Devices), and MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers).
Together, these elements protect you from electric shocks, prevent overloaded circuits, and isolate electrical faults before they become dangerous.
Credit: eFIXX
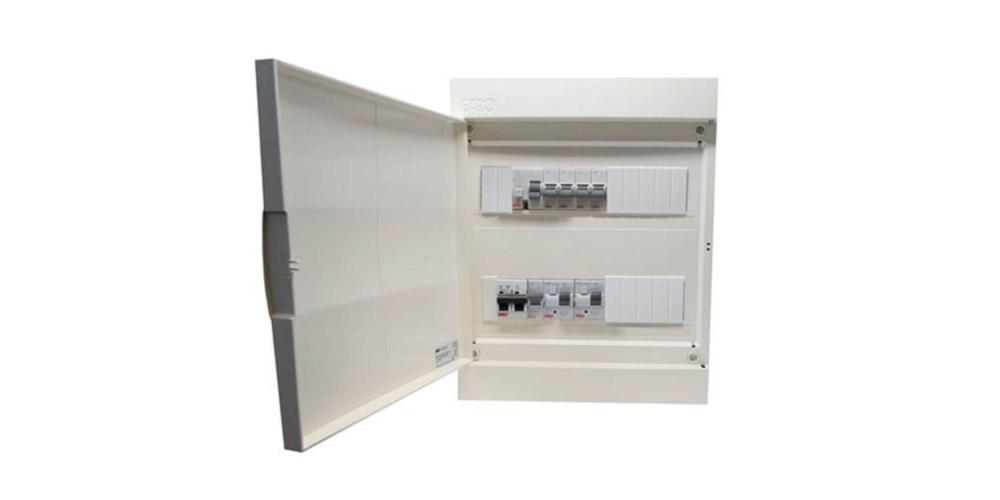
Components of a Consumer Unit
Understanding the internal parts of your consumer unit helps you appreciate its function and importance. Here's a breakdown of each core component:
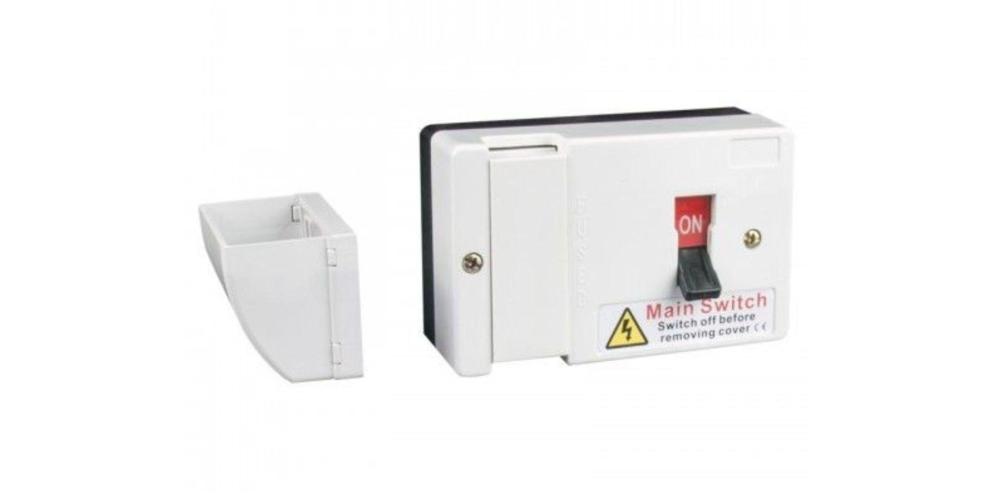

Main Switch
This is the master control for all the circuits in your home or business. In an emergency, you can shut off all electricity with this single switch, offering crucial protection.
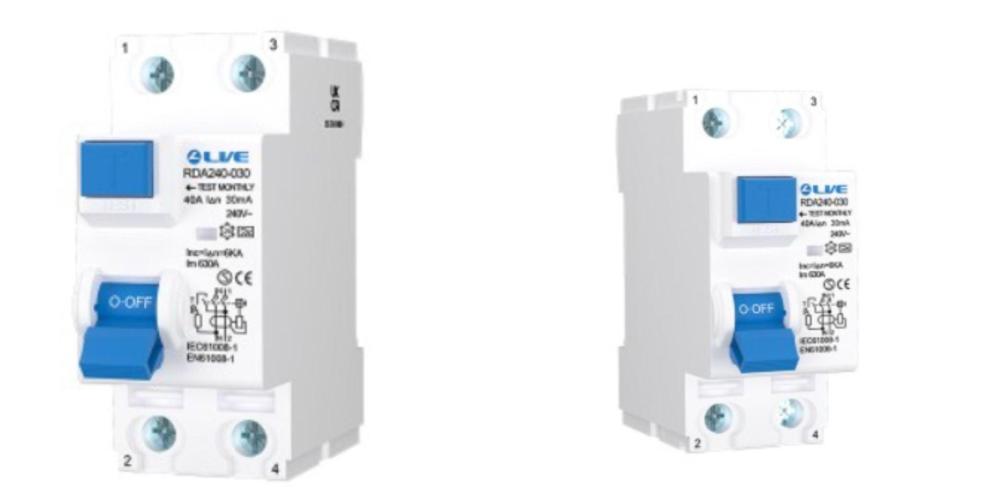

RCD (Residual Current Device)
RCDs monitor the current balance in live and neutral wires. If they detect a fault — like current leaking through a person — they disconnect the circuit immediately, preventing electrocution.
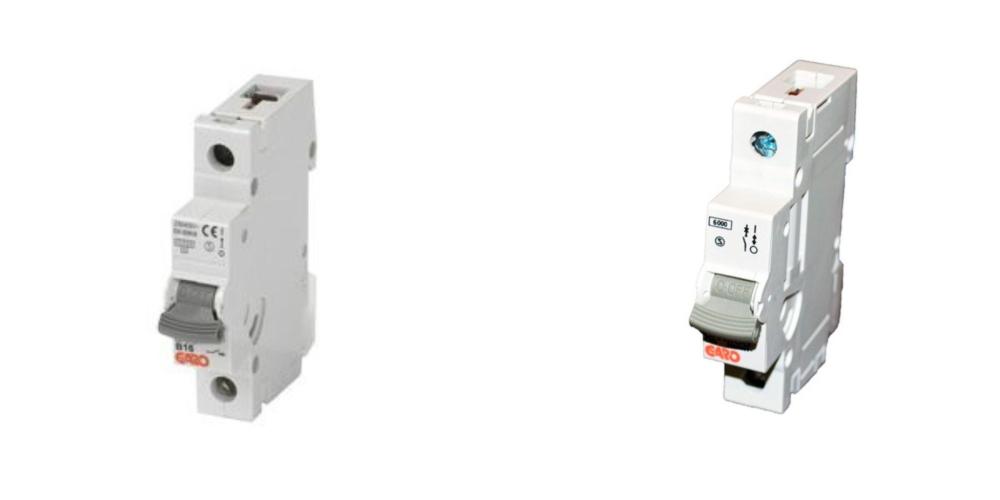

MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
Each MCB protects an individual circuit (like lighting or sockets). If a circuit is overloaded or short-circuited, the MCB trips to cut the power and prevent fires.
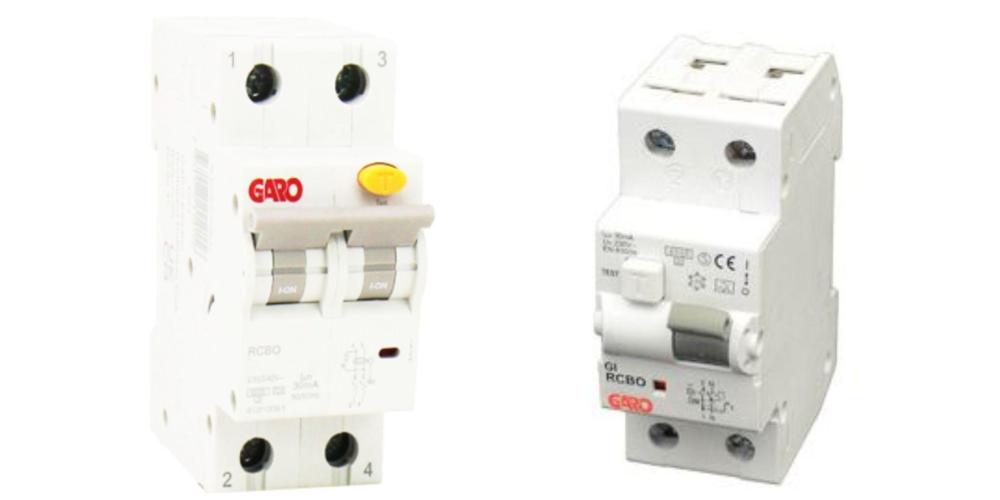

RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent Protection)
An RCBO combines the safety of an RCD and MCB in one unit. It’s particularly useful for mission-critical appliances where you need both earth leakage and overload protection on a single circuit.
Types of Consumer Units

Different spaces require different setups. Below are the common types of consumer units and where they’re best used.
High Integrity Consumer Units
These units feature three neutral bars, allowing you to combine RCDs and RCBOs efficiently. This setup lets you isolate sensitive circuits — like freezers or alarms — preventing nuisance tripping and offering maximum protection.
Split Load Consumer Units
Split load units contain both RCD-protected and unprotected circuits. A cost-effective solution, they’re ideal for small to medium domestic properties. They’re often used in compliance with modern regulations, allowing you to separate high-risk circuits.
Garage Consumer Units
Designed for garages, sheds, or workshops, these compact units handle fewer circuits (usually 2–5). Despite their small size, they’re robust and essential for outbuildings to remain safe and functional.
Credit: ERES Electrical
Choosing the Right Consumer Unit

Selecting the right unit depends on a few key factors:
Load Capacity
Think about your power demand. For a standard home, a split load consumer unit may suffice. For a larger property or business, a 3-phase distribution board may be necessary to support high-current appliances.
Type of Installation
Where will it be used? A compact unit may work for domestic use, while larger units are needed for commercial setups. Garage units are perfect for outbuildings.
Compliance with Standards
Always choose units that comply with UK or ROI regulations. Not only is this vital for safety, but it’s also required for home sales, renovations, and insurance.
Installation and Safety Tips
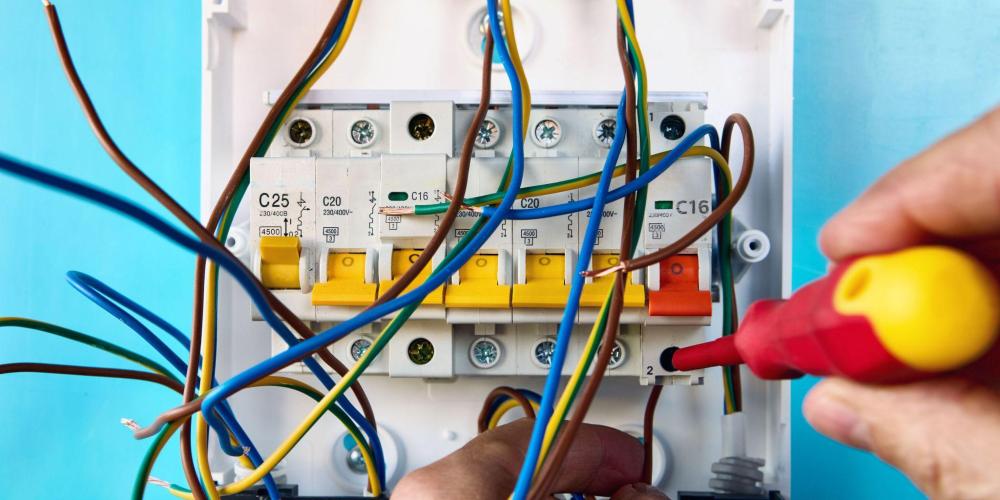

To ensure your consumer unit performs safely, follow these best practices:
Hire a Qualified Electrician
Installing or upgrading a consumer unit is not a DIY task. A certified electrician ensures compliance with Part P of Building Regulations.
Regular Maintenance
Inspect the unit regularly. Loose connections or tripped breakers can signal deeper issues. Preventive maintenance helps avoid faults and ensures everything is operating efficiently.
Avoid Overloading Circuits
Overloading a circuit is a common fire risk. Use the correct breakers and fuses for the appliances you plan to use on each circuit.
Upgrading Your Consumer Unit
Older fuse boxes often lack modern safety features. Here’s when you should consider an upgrade:
- Your current unit still uses rewirable fuses
- You’ve installed new appliances or added rooms
- Your home fails to meet new building regulations
- You’ve experienced frequent breaker trips
Upgrading typically includes:
- Isolating the power supply
- Installing a new metal-clad consumer unit
- Testing all connections
- Issuing an Electrical Installation Certificate
Electrical Consumer Unit Regulations
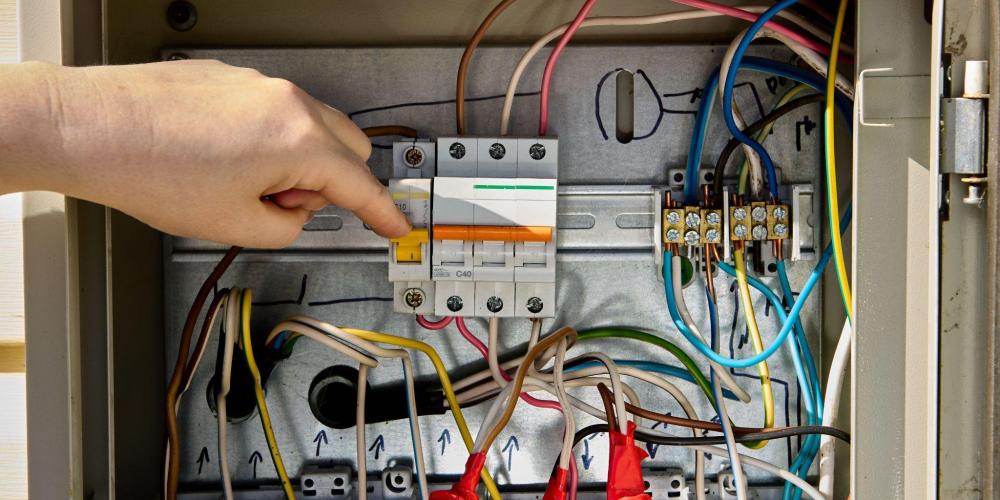
Both the UK and the Republic of Ireland have specific regulations regarding installation and operation:
UK Regulations (IET Wiring Regulations - BS 7671)
- All units must be enclosed in non-combustible enclosures (typically metal)
- Units must be mounted between 1350mm and 1450mm from floor level
- RCDs are required for most circuits in domestic properties
ROI Regulations (I.S. 10101)
- Double Pole Isolator Switch is required
- RCD protection must cover all luminaire circuits
- Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) are mandatory or must be excluded via risk assessment
- Enhanced protection required for final AC circuits
Meteor Electrical supplies Garo consumer units that comply with ROI standards, including:
- 2 Row 7 Way Consumer Unit with Main B63 MCB (Type A)
- 2 Row 7 Way Consumer Unit with Main B63 MCB (Type B)
Find Your Consumer Unit at Meteor Electrical
Small Consumer Units
Ideal for garages, flats, or smaller homes. Our selection ranges from 2-way to 18-way units, built for domestic setups with lower load requirements.
Large Consumer Units
Perfect for commercial or large residential properties. These come in sizes up to 75 ways and support high-load configurations. For 3-phase setups, check out our TP&N distribution board range.
Consumer Unit Accessories
From RCDs to trunking and surge protectors, we stock every accessory to complete your installation — all in one place.
Explore the full range of consumer units and accessories on Meteor Electrical.
Conclusion
Understanding how a consumer unit works — and choosing the right one — is essential for protecting your property and staying compliant with modern standards. From selecting the correct type to maintaining and upgrading your setup, each step plays a role in ensuring long-term electrical safety.
At Meteor Electrical, we offer a wide range of BSI-certified consumer units, garage units, and all the accessories you need for a safe and compliant installation. Whether you're a professional electrician or a homeowner planning an upgrade, we’re here to help every step of the way.
Shop our full selection of consumer units and accessories at Meteor Electrical — or contact our expert team for tailored advice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between a consumer unit and a distribution board?
A consumer unit is a type of distribution board used in domestic properties. It contains protective devices like MCBs, RCDs, and RCBOs, and is designed to control and protect household electrical circuits. A distribution board, on the other hand, is a broader term that applies to both residential and commercial or industrial electrical systems, often accommodating more complex or high-load requirements.
2. Can I have two electric showers in one house?
Yes, it’s possible to install two electric showers in a single property, but it requires careful load planning. A qualified electrician must evaluate the current consumer unit capacity, circuit protection, and mains supply. You may need a unit upgrade or a dedicated circuit for each shower to comply with safety regulations and avoid overloads.
3. What are the different types of bathroom extractor fans?
Bathroom extractor fans are available in various types, including wall-mounted, ceiling-mounted, and window-mounted models. Key features to consider include humidity sensors, timer functions, and silent operation. Choose a fan based on room size, moisture levels, and placement to ensure effective ventilation and mould prevention.
4. What is an IP rating, and why is it important?
An IP rating (Ingress Protection rating) defines how well an electrical device is protected against dust and moisture. For example, IP65 indicates complete protection against dust and resistance to low-pressure water jets. IP ratings are crucial when selecting outdoor sockets, lights, or bathroom components, where environmental exposure is a factor.
5. When should I upgrade my consumer unit?
You should consider a consumer unit upgrade if your current unit lacks RCD protection, shows signs of wear, or cannot support modern electrical loads. Upgrading is also essential when renovating, adding high-power appliances (like EV chargers), or if your system doesn’t meet current BS 7671 wiring regulations. Always consult a qualified electrician to assess your system.

